
Japan has the best healthcare in the world according to the latest report from the Legatum Institute. We take a look at who else performed well
If you’re one of the millions of people working remotely or following a career as a digital nomad, then access to quality healthcare will undoubtedly be one of the most important factors in your choice of destination.
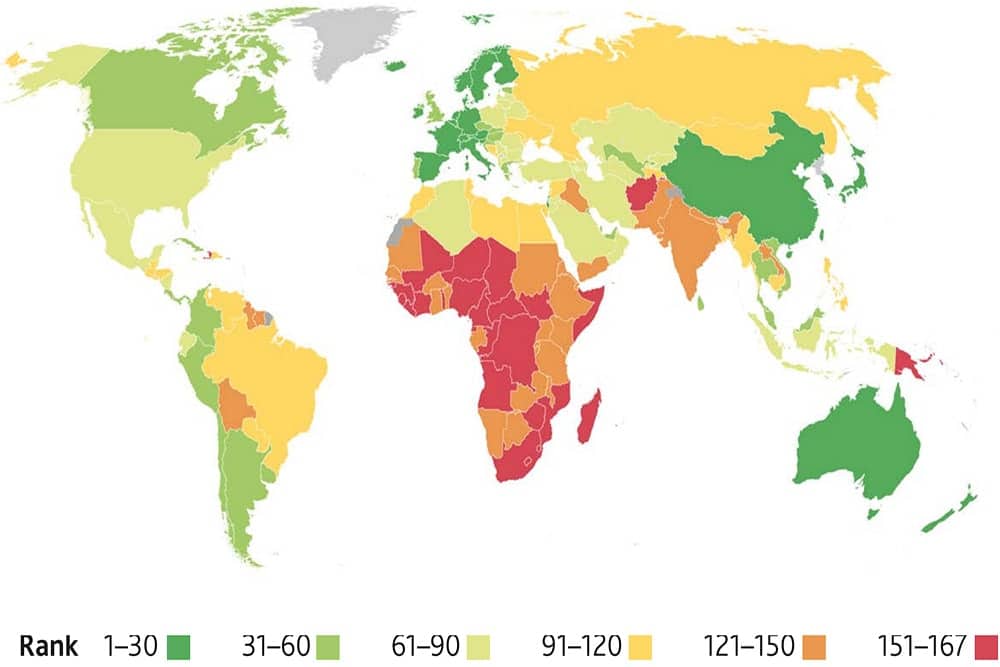
According to the Legatum Institute, a UK-based think tank and charity focused on lifting people out of poverty, Japan has the best healthcare in the world, followed by Singapore, South Korea, Norway and Taiwan.
Now in its 15th year, the institute’s Prosperity Index ranks countries in regard to prosperity and development based on 12 sub-indexes, or ‘pillars’, one of which is health.
Evaluating healthcare
The Prosperity Index sources data from a number of organisations including UNICEF, the World Health Organisation, the International Labour Organization and the United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS to assess the quality of healthcare systems in 167 countries and territories.
It measures the extent to which people are healthy and can access the necessary services to maintain good health including treatment, care systems, preventative measures, provisions for mental health illness, risk factors and mortality rates.
best healthcare in the world
Since last year, Japan has taken top spot, pushing Singapore into second place. Taiwan has lept 13 places to fifth position, meaning four of the top five countries are in Asia.
Meanwhile, the USA has slipped nine places from 59th to 68th despite spending more on healthcare than other high-income nations. The UK has fallen six places from 25th to 31st following years of underfunding.
The following 10 countries have been assessed as providing the best healthcare for their population.
“For a nation to truly prosper, its citizens must have good health. Those who enjoy good physical and mental health report high levels of wellbeing. An effective health infrastructure is critical for sustaining per capita income. Poor health keeps people from fulfilling their potential.”
– Baroness Philippa Stroud, CEO of the Legatum Institute
The Legatum Institute draws on years of data to evaluate which countries have improved the most. A number of factors contribute to improving healthcare in a country.
These factors include:
- Behavioural Risk Factors
- Preventative Interventions
- Care Systems
- Mental Health
- Physical Health
- Longevity
One obvious factor is longevity (life expectancy). The life expectancy of people in Zimbabwe has increased by more than 15 years from 2009 to 2019, more than in any other country.
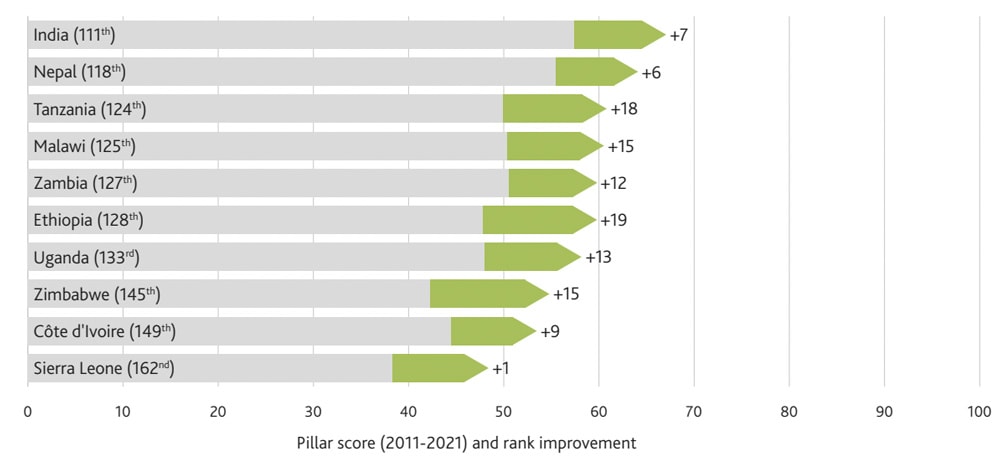
It was noteworthy that the report found that although the region continues to lag behind all others, eight out of the 10 of the most improved nations since 2011 were all African.
The countries with the weakest healthcare were as follows:
- Central African Republic
- South Sudan
- Chad
- Lesotho
- Somalia
- Sierra Leone
- DR Congo
- Eswatini
- Liberia
- Nigeria
Healthcare during a pandemic
The planet has seen near-universal progress in health over the past decade, with all but 12 countries seeing an improvement during that time.
In particular, expansions in immunisation programmes have resulted in a greater proportion of the global population being inoculated against life-threatening diseases.
This, combined with antenatal care now covering over 90% of women across the globe, has led to the improvement observed in preventative care.
“There is never a good time for a global health crisis, but if there has to be one, the progress that has been made over the last decade provides emerging nations with a better context in which to tackle it.”
– Baroness Philippa Stroud, CEO of the Legatum Institute
However, these improvements came under threat as the health of many nations were put under considerable strain due to the coronavirus pandemic.
Initially, a particular concern was how nations with poorer healthcare systems would cope with the virus. However, we now know that the virus disproportionately affects the elderly and those with underlying health conditions.
This demographic is generally more commonly found in more developed countries. For example, the median age in Italy is 47.3, whereas the median age across Africa is around 20. Similarly, the obesity rate in the USA stands at over 40%, compared to around 15% in Africa.
As such, it is generally the health systems of more developed nations that have been in greater danger of being overwhelmed.
Types of healthcare
Countries around the globe take vastly different approaches to providing healthcare to their population. Many developed countries have universal government-funded healthcare (also known as single-payer healthcare).
In this system, healthcare is available to all citizens regardless of their income or employment status. This system is used by countries such as Australia, Canada, Norway, Singapore and the UK.

Another popular option is to use a universal public insurance system where the government usually withholds part of workers’ wages which goes towards healthcare insurance. This system is used by China, France, Japan and South Korea among others.
Several nations, including the Netherlands and Switzerland, use a universal private health insurance system. Low-income citizens who cannot afford insurance are then subsidised by the government.
You may also like:
► Best cities in the world
► Most dangerous countries in the world
► Countries with the best healthcare in the world
► Best countries for women
► Happiest countries in the world
► World’s most powerful passport
► Countries with the fastest internet in the world
► Most stressed countries in the world
A final group of countries, which includes the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia and the USA, uses a non-universal insurance system.
In this case, some citizens have private health insurance, some may receive subsidised public healthcare, while some are not insured at all.
best healthcare in the world 2023: complete rankings
The health pillar of Legatum’s report measures a country’s performance in three areas: basic physical and mental health, health infrastructure and preventative care.
NB: Some countries and territories have been excluded due to insufficient data.
| Rank | Country | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Japan | 86.6 |
| 2 | Singapore | 86.1 |
| 3 | South Korea | 84.1 |
| 4 | Norway | 84.0 |
| 5 | Taiwan | 83.4 |
| 6 | Israel | 82.8 |
| 7 | China | 82.8 |
| 8 | Iceland | 82.3 |
| 9 | Netherlands | 82.2 |
| 10 | Sweden | 82.1 |
| 11 | Malta | 81.7 |
| 12 | Luxembourg | 81.5 |
| 13 | Switzerland | 81.5 |
| 14 | Finland | 81.4 |
| 15 | Hong Kong | 81.3 |
| 16 | Germany | 81.1 |
| 17 | Italy | 81.1 |
| 18 | Denmark | 80.6 |
| 19 | Belgium | 80.6 |
| 20 | France | 80.5 |
| 21 | Spain | 80.5 |
| 22 | Australia | 80.2 |
| 23 | Slovenia | 80.2 |
| 24 | New Zealand | 79.7 |
| 25 | Austria | 79.6 |
| 26 | Ireland | 79.5 |
| 27 | Thailand | 79.4 |
| 28 | Cyprus | 79.1 |
| 29 | Cuba | 79.0 |
| 30 | Czechia | 79.0 |
| 31 | UK | 78.8 |
| 32 | Colombia | 78.7 |
| 33 | Costa Rica | 78.4 |
| 34 | Canada | 78.4 |
| 35 | Uruguay | 78.1 |
| 36 | UAE | 77.8 |
| 37 | Seychelles | 77.8 |
| 38 | Portugal | 77.6 |
| 39 | Qatar | 77.6 |
| 40 | Sri Lanka | 77.3 |
| 41 | Estonia | 77.3 |
| 42 | Argentina | 77.2 |
| 43 | Slovakia | 77.0 |
| 44 | Malaysia | 77.0 |
| 45 | Kuwait | 76.9 |
| 46 | Greece | 76.8 |
| 47 | Vietnam | 76.5 |
| 48 | Panama | 76.5 |
| 49 | Peru | 76.4 |
| 50 | Uzbekistan | 76.3 |
| Rank | Country | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 51 | Hungary | 76.3 |
| 52 | Croatia | 76.1 |
| 53 | Chile | 75.7 |
| 54 | Bahrain | 75.4 |
| 55 | Belarus | 75.3 |
| 56 | Poland | 75.2 |
| 57 | Oman | 75.2 |
| 58 | Turkey | 75.1 |
| 59 | Turkmenistan | 74.9 |
| 60 | Jamaica | 74.9 |
| 61 | Iran | 74.8 |
| 62 | Romania | 74.7 |
| 63 | Bulgaria | 74.7 |
| 64 | Saudi Arabia | 74.5 |
| 65 | Armenia | 74.5 |
| 66 | Trinidad & Tobago | 74.1 |
| 67 | Lithuania | 74.1 |
| 68 | USA | 73.9 |
| 69 | North Macedonia | 73.9 |
| 70 | Albania | 73.8 |
| 71 | Kazakhstan | 73.8 |
| 72 | Latvia | 73.8 |
| 73 | Kyrgyzstan | 73.4 |
| 74 | Azerbaijan | 73.4 |
| 75 | Serbia | 73.3 |
| 76 | Nicaragua | 73.0 |
| 77 | Jordan | 72.9 |
| 78 | Ecuador | 72.9 |
| 79 | Mexico | 72.7 |
| 80 | Indonesia | 72.7 |
| 81 | Algeria | 72.5 |
| 82 | Belize | 72.4 |
| 83 | Mauritius | 72.4 |
| 84 | Moldova | 72.3 |
| 85 | Dominican Rep | 72.1 |
| 86 | Brazil | 72.0 |
| 87 | Cabo Verde | 71.9 |
| 88 | Morocco | 71.7 |
| 89 | Russia | 71.6 |
| 90 | Tajikistan | 71.5 |
| 91 | Paraguay | 71.4 |
| 92 | Tunisia | 71.4 |
| 93 | Georgia | 71.3 |
| 94 | Cambodia | 71.2 |
| 95 | Montenegro | 70.6 |
| 96 | São Tomé & Príncipe | 70.5 |
| 97 | Venezuela | 70.5 |
| 98 | Bosnia & Herzegovina | 70.0 |
| 99 | El Salvador | 69.7 |
| 100 | Lebanon | 69.7 |
| Rank | Country | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Philippines | 69.7 |
| 102 | Bangladesh | 69.0 |
| 103 | Honduras | 68.7 |
| 104 | Ukraine | 68.7 |
| 105 | Guatemala | 68.2 |
| 106 | Myanmar | 67.7 |
| 107 | Mongolia | 67.7 |
| 108 | Libya | 67.5 |
| 109 | Egypt | 67.2 |
| 110 | Syria | 67.1 |
| 111 | India | 67.1 |
| 112 | Bolivia | 65.9 |
| 113 | Iraq | 65.5 |
| 114 | Rwanda | 65.2 |
| 115 | Kenya | 64.6 |
| 116 | Laos | 64.6 |
| 117 | Ghana | 64.2 |
| 118 | Nepal | 64.1 |
| 119 | Suriname | 63.9 |
| 120 | Senegal | 63.4 |
| 121 | Guyana | 62.9 |
| 122 | Djibouti | 62.4 |
| 123 | Sudan | 60.9 |
| 124 | Tanzania | 60.8 |
| 125 | Malawi | 60.5 |
| 126 | Namibia | 59.9 |
| 127 | Zambia | 59.8 |
| 128 | Ethiopia | 59.8 |
| 129 | Comoros | 59.8 |
| 130 | Pakistan | 59.5 |
| 131 | Botswana | 59.5 |
| 132 | Burkina Faso | 59.1 |
| 133 | Uganda | 58.2 |
| 134 | Mauritania | 58.0 |
| 135 | Burundi | 57.8 |
| 136 | Eritrea | 57.5 |
| 137 | Yemen | 57.0 |
| 138 | Gabon | 56.8 |
| 139 | Benin | 56.7 |
| 140 | South Africa | 56.6 |
| 141 | The Gambia | 56.1 |
| 142 | Madagascar | 55.5 |
| 143 | Togo | 54.9 |
| 144 | Congo | 54.8 |
| 145 | Zimbabwe | 54.8 |
| 146 | Mali | 54.4 |
| 147 | Papua New Guinea | 54.2 |
| 148 | Niger | 54.1 |
| 149 | Côte d’Ivoire | 53.5 |
| 150 | Mozambique | 53.1 |
| 151 | Haiti | 52.7 |
| 152 | Guinea-Bissau | 51.2 |
| 153 | Afghanistan | 51.0 |
| 154 | Cameroon | 50.7 |
| 155 | Equatorial Guinea | 50.5 |
| 156 | Guinea | 50.4 |
| 157 | Angola | 50.3 |
| 158 | Nigeria | 49.1 |
| 159 | Liberia | 49.1 |
| 160 | Eswatini | 49.0 |
| 161 | DR Congo | 48.6 |
| 162 | Sierra Leone | 48.4 |
| 163 | Somalia | 43.3 |
| 164 | Lesotho | 40.7 |
| 165 | Chad | 37.7 |
| 166 | South Sudan | 35.5 |
| 167 | Central African Rep | 32.8 |
The latest Legatum Prosperity Index can be downloaded here.






